With more than 400 million native speakers, Arabic is one of the most spoken languages worldwide and among the top influential languages in business.
This huge number of speakers, scattered across the Middle Eastern and African regions, has led to a vast diversity of Arabic dialects.
However, this linguistic diversity can present a challenge for businesses entering the Arabic-speaking world. They face a crucial decision: which form of Arabic should they use when translating their content, and can these translations be used across different markets?
Selecting the right form of Arabic will help you reach the ideal audience for your business. Meanwhile, choosing the wrong one can lead to misinterpretations, missed opportunities, and even cultural faux pas.
This guide will help you make the right decision by explaining everything you should know about Arabic dialects and choosing the perfect one for your translation project. So, let’s jump into it!
Let’s Unpack the Arabic Language Variations
First, let’s start by clearing out the confusion around the different Arabic variations to help you navigate your choices correctly.
Classical Arabic & Modern Standard Arabic
Classical Arabic (CA) is the standardized written and spoken form that emerged alongside the rise and spread of Islam as the language of the Holy Quran.
While the influence of classical Arabic has been powerful in shaping Arabic literature for decades, this form of Arabic no longer reflects everyday language.
Due to the complex morphological and syntactical nature of classical Arabic, Arabic speakers shifted towards using Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) over the years.
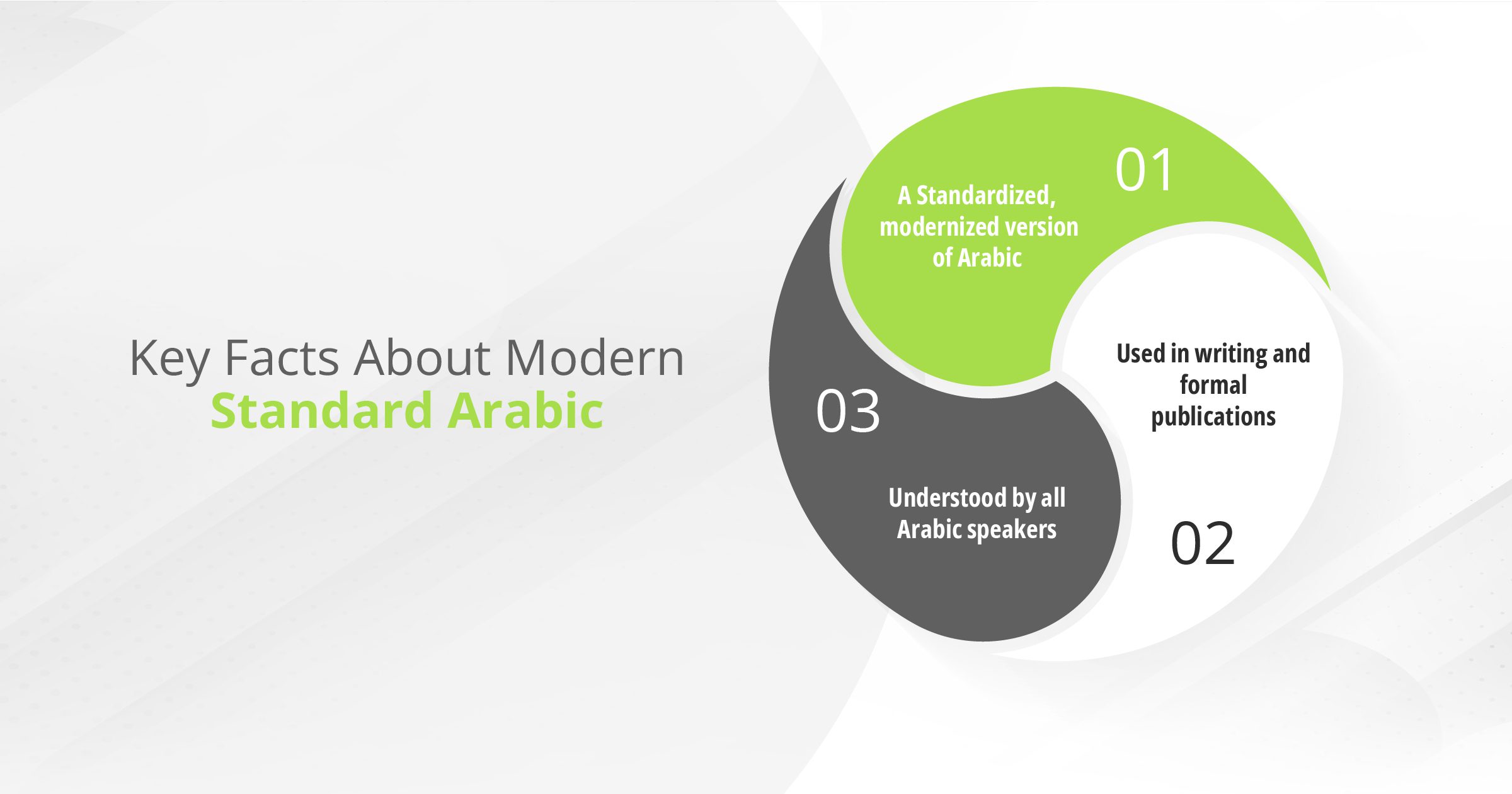
So, what is Modern Standard Arabic (MSA)?
As its name suggests, Modern Standard Arabic is the modernized written form of Classical Arabic. While MSA builds upon classical Arabic, they still differ in certain aspects, like vocabulary and writing style.
Given its simplified form, MSA serves as the language of formal writing and speech used in education, government, literature, and media across the Arab world today.
What is interesting about MSA is that it provides a common language that all Arabic speakers, regardless of their country of origin or local dialect, can understand.
What’s more, it bridges the gap between millions of people who are native speakers and those who learn Arabic as a second language.
The Different Arabic Language Dialects
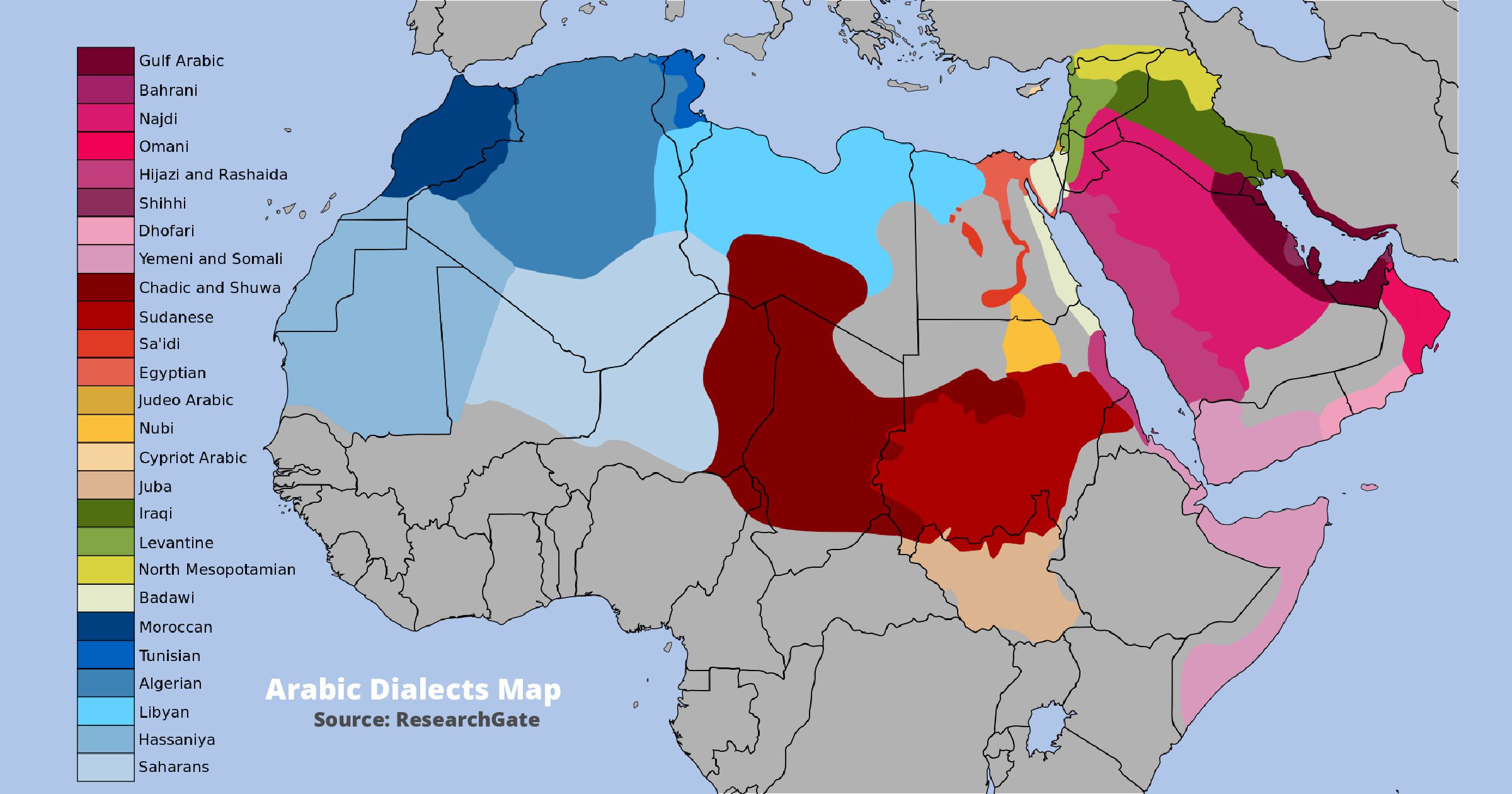
Arabic is the official language of 22 countries. This vast geographic spread has resulted in the evolution of 25 distinct Arabic dialects, each shaped by centuries of influence from local environments and cultures.
Although Modern Standard Arabic remains the written standard shared across Arabic-speaking regions, colloquial Arabic varies significantly from one area to another.
One of the major differences between Arabic dialects is that the pronunciation of specific letters can change from one dialect to another.
For instance, when it comes to a word like “جميل” (Beautiful), certain dialects use the ‘j’ sound, as in “Jameel”, while others use the ‘g’ sound, as in “Gameel.”
Additionally, beyond pronunciation, each Arabic dialect has its own unique vocabulary, idiomatic expressions, and slang terms. This linguistic nuance is particularly important for businesses aiming to connect with local audiences.
Imagine, for example, running a store that sells cat food. As you can see in the table below, the Arabic word for “cat” takes on surprisingly different forms depending on the dialect. So, when marketing your product, you have to be mindful and use the term that resonates most with your target audience.
Dialect | Masculine Word | Feminine Word |
Egyptian Arabic | qit – قط | qitta – قطة |
Lebanese Arabic | bsenie – بسيني | bsena – بسينة |
Tunisian Arabic | qatos – قطوس | qatosa – قطوسة |
Gulf Arabic | bis – بس Hirr – هر | bisa – بسة Hirra – هرة |
Iraqi Arabic | bzon – بزون | bzonh – بزونة |
Yemeni Arabic | Demma – دمة | Demma – دمة |
Moroccan Arabic | msh – میش | Msha – ميشة |
A Closer Look at the Most Prominent Arabic Dialects
The Arabic dialects are categorized into six major groups as follows:
- Egyptian Arabic: Egypt (exclusively)
- Moroccan Arabic: Algeria, Morocco, Tunisia, Mauritania, and Western Sahara
- Levantine Arabic: Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Palestine
- Gulf Arabic: Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates
- Iraqi Arabic: Iraq, Syria, and Kuwait
- Yemeni Arabic: Yemen and southwestern Saudi Arabia
However, it’s crucial to understand that Arabic varieties exist within each dialect group. This means the spoken language you hear in a particular Arabic city can differ significantly from the one spoken in rural communities.
How to Choose the Right Arabic Dialect for Your Business Translation
To figure out which form of Arabic is ideal for your translation project, ask yourself one question:
What type of content are you translating, and what’s the intended use?
Now, let’s walk you through the different scenarios you may encounter.
Complex & Technical Content Translation
Modern Standard Arabic is suitable for conveying complex information as it ensures a high level of clarity and consistency.
So, if you have documents that require a formal tone, precision, and adherence to standard language norms, translate them into MSA. This includes official company policies, legal contracts, user manuals, scientific reports, product specifications, etc.
Official Document Translation
When translating documents for government institutions, international organizations, or even private sector operations, opt for MSA. This will ensure that your content aligns with the established linguistic standards and is widely understood.
Advertising and Marketing Translation
If you want to translate marketing materials, ad campaigns, and social media content, use your target audience’s local dialect.
The purpose of marketing materials is to connect and resonate with potential customers on an emotional level, often using a casual and informal tone.
And by speaking to your audience in their local dialect, your messaging will feel more familiar, relatable, and engaging and is more likely to improve the effectiveness of your marketing efforts.
Website Translation
When translating your company’s website, it’s generally recommended to use MSA to maintain a professional tone and make it accessible to a broader audience.
Plus, when users search for information in Arabic, they tend to use MSA keywords. So, having your content in MSA can improve its visibility on search engines and attract more organic traffic.
However, in some cases, you can present certain content in the local dialect, such as customer testimonials. This is because keeping the feedback in its original dialect adds authenticity and relatability.
Moreover, if your website offers live chat support, using the local dialect can create a more friendly experience for users from specific regions.
The Bottom Line
When building your translation strategy for Arabic-speaking markets, you don’t always have to choose one Arabic variation over the other.
You just need to know when to use each – based on the content type and purpose.
As a rule of thumb, opt for MSA when translating official content intended for professional business purposes or addressing a broad audience across the Arab world.
But go for local dialects when localizing marketing and advertising content aimed at connecting with regional audiences.
bayantech: A Leading Translation & Localization Agency in the Middle East
Looking for a translation agency capable of dealing with different Arabic dialects translation? Based in the United Arab Emirates and well-established as one of the leading Arabic translation service providers in the Middle East, bayantech is ready to meet your Arabic translation needs.
We are equipped with human experts and the latest translation tools to deliver native modern standard Arabic and different Arabic dialect translations across all industries and with extensive language pair coverage.
Our agency has been in the language services market and has been working for the best companies in MENA for almost twenty years. Being ISO 17001 and 9001 certified and working with a team of native Arabic translators for every dialect, bayantech makes the ideal partner for your business.
Get in touch with our team and let’s discuss your upcoming Arabic translation project.
8 Steps Every Medical Interpreter Takes
Looking for a medical interpreter? Discover the career path of medical interpreters and qualifications they need to acquire to take on interpreting jobs.