Today, Google Translate allows you to get massive amounts of translations done instantly and with no charges. This is a dream come true for businesses looking for budget-friendly translation solutions.
But, of course, you have to think about the accuracy of Google Translate (or any Machine Translation) and whether it lives up to your expectations…
Well, the question of can you trust Google Translate accuracy or not depends on several factors, such as the language pair and intended use of translation.
In this blog post, we’ll dig deep into how neural machine translation engines, like Google, work and discuss how reliable they can be.
We’ll also provide some guidance on the perfect use cases for Google Translate and its peers. So, let’s get into it!
How Google Translate Works
First, let us give you a quick overview of how Google Translate works.
Statistical Machine Translation (SMT)
When Google Translate (GT) was first launched in 2006, it relied on an approach called Statistical Machine Translation (SMT). SMT works by translating small units of the input text, like words and phrases.
Let’s say, for example, you input an English text and want to translate it into the Spanish language.
GT would search for each individual phrase within its publicly available translation data and look for its equivalent in Spanish. If a particular word has multiple possible translations, GT would identify the most common translation based on how often it appears in the data.
Then, it selects this most common translation for the word without considering the context in which the word is used.
This process is repeated for each word in the input text. As a result, these word-for-word translations were not so accurate and often sounded odd or lacked nuance.
[Google] Translate was really limited by the data that was available, and it couldn’t read semantics or context very well.
— Abu Shah, Google Translate Engineer
Neural Machine Translation (NMT)
10 years later, Google introduced Google Neural Machine Translation (GNMT) technology, using a more advanced machine learning system.
NMT models are trained on a vast amount of parallel text data, which means large volumes of text in one language and their translations in another.
Then, NMT engines use artificial neural networks to process the text in the source language and automatically generate translations in the target language.
Unlike the phrase-based SMT, this approach considers the entire sentence as a whole, allowing it to capture the context and meaning of the entire sentence.
Of course, after extensively training the NMT models and enhancing their accuracy, this framework led to more precise, human-like translations.
According to Google, NMT reduced translation errors by more than 55% to 85% across many language pairs.
What’s more, after developing GNMT, they also eliminated the need to use English as a bridging language when translating between t wo languages, introducing a zero-shot translation method.
This means GT can generate direct translations between any language pair without translating the input in English first and then translating the English output in the target language.
Measuring Google Translate Accuracy
Now, the question you’re here for: How accurate is Google Translate? And can you trust it?
Well, the accuracy of Google Translate varies significantly depending on the specific language pair.
- In a study by UCLA Medical Center, they used GT to translate 20 emergency department discharge instructions in 7 different languages (Spanish, Chinese, Armenian, Tagalog, Vietnamese, Korean, and Farsi).
They then evaluated the translation accuracy. How did GT perform?
The average Google Translate accuracy was 82.5%. However, this number ranged from 55% to 94% across languages.
For instance, GT was most accurate for Spanish. Meanwhile, the lowest accuracy was in Armenian, followed by Farsi and Vietnamese.
- In another study by Nottingham Children’s Hospital, they assessed Google Translate accuracy by translating ten common medical statements into 26 languages. The results showed that 57.7% of the translations were accurate, while 42.3% were incorrect.
They also measured the accuracy level for each language group, and the findings were as follows:
| Language group | Google Translate accuracy percentage |
| Western European | 74% |
| Eastern European | 62% |
| Asian languages | 46% |
| African languages | 45% |
Key Takeaway
The above-mentioned studies suggest that Google Translate generally achieves higher accuracy when translating between English and European languages compared to Asian and African languages. Why?
Well, because European languages are considered high-resource languages, meaning that there is more training data available online for these languages.
As a result, translations involving high-resource languages tend to sound more natural than translations involving languages that have limited training data.
Are Other Online Translation Tools More Accurate than Google Translate?
Now comes the question: if Google Translate doesn’t always have a high accuracy rate, do other translation tools outperform Google?
Well, although Google Translate is a widely used and capable MT tool, it faces strong competition from alternatives.
According to Intento’s 2024 report, the quality of different machine translation (MT) engines varies substantially by language pair and domain.
But Intento’s evaluation shows that DeepL ranks the highest across 11 language pairs and 9 domains. Google came in second place, followed by Amazon Translate and Microsoft Translator.
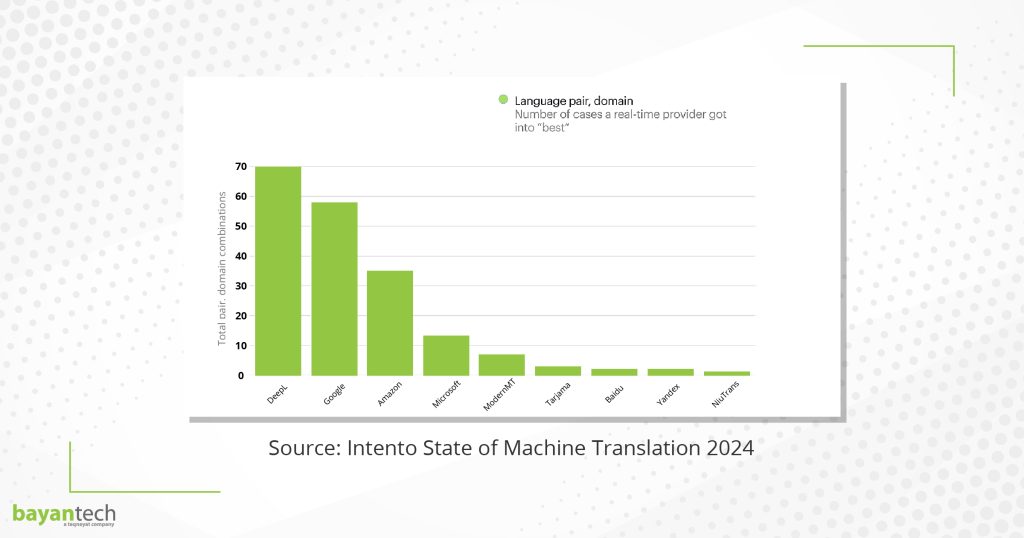
Source: Intento State of Machine Translation 2024
Additionally, the report highlights that most MT engines tend to struggle with translations in the entertainment and colloquial domains. This is likely due to the nuanced tone, cultural references, and idiomatic expressions commonly used in these domains.
To sum up, despite Google and DeepL being top choices when it comes to MT, both still have their limitations depending on the content nature and language you’re targeting.
When to Use (and When NOT to Use) Google Translate
It’s important to understand the appropriate use cases of Google Translate or any other machine translation tool.
So, we’ve identified 3 scenarios where you can use GT and 3 where it’s best to avoid using it.
Use Google Translate For:
- Casual communications
Google Translate is most suitable for personal use and informal communications. Also, you can rely on it for translating internal company documents where perfect accuracy isn’t crucial.
- Low-visibility, low-impact content
When translating customer-facing content that has low visibility and won’t significantly impact your brand reputation, GT can be a viable option. This includes customer support content, product descriptions, FAQs, contact information, etc.
- Large volumes of content
If you have large volumes of text that you need to translate quickly without a heavy cost, Google Translate can be a helpful tool.
However, for high-importance content, GT should only serve as an initial step, followed by post-editing. (Keep reading to learn about the role of human editing!)
Don’t Use Google Translate For:
- High-visibility content
For high-visibility customer-facing content, like blog posts, brochures, or user manuals, solely relying on Google Translate without human review is a big no.
Machine translations can be riddled with inaccuracies that could damage your brand image and push away potential customers from your business.
- Sensitive, highly regulated domains
When translating sensitive content, such as medical, scientific, or politically charged text, you should also avoid Google Translate.
It’s critical to ensure that these types of content are translated with the highest level of accuracy and clarity—which you can only achieve through the expertise of human translators.
- Creative translation
For creative text like literature, marketing, advertising, or entertainment content, human intervention is essential. This type of content is often context-dependent and includes references deeply rooted in local cultures.
As such, you must rely on creative human experts to craft translations that convey the original tone, maintain emotional impact, and touch the hearts of target audiences.
The Importance of Human Review and Editing
While Machine Translation has its perks (fast and affordable), it also has its limitations in terms of accuracy and contextual understanding.
That’s why MT can only be reliable when it’s paired with the human touch in post-editing.
Machine Translation Post-Editing (MTPE) refers to the process of editing and refining the raw MT output to improve its accuracy, clarity, consistency, and cultural relevance.
MTPE ensures that your translations are linguistically accurate, technically sound, and free of any misinterpretations. More importantly, human editing helps you catch any biases or culturally insensitive messages that could potentially harm your business.
And lastly, human reviewers can adjust the tone and style of translated content to match your brand’s voice and values—something machines fail to do.
Want to Strike a Balance between Translation Cost and Quality? We Can Help!
bayantech is a leading translation services provider with a track record of 20 years of experience helping global brands strengthen their international presence.
We provide professional machine translation as well as MTPE solutions, tailored to meet the specific needs of businesses like yours. If you’re struggling to achieve a balance between translation quality and cost, we’ve got you covered!
Request a quote now and enter the language pairs and your project needs and we’ll get back to you with a customized translation plan.