If you want your brand to reach its maximum potential, the concept of globalization is probably no stranger to you. You might already have considered expanding your company to foreign markets.
And while there are several ways of reaching your target audience, social media platforms are a fundamental ingredient in any digital marketing menu.
In this article, we will uncover our best advice when it comes to translating your social media content into multiple languages. Whether you’re looking for a translation company, or still trying to gain an understanding of the power of social media translation for your business, you’re bound to find a useful tip below. Without further ado, let’s get started.

What Is Social Media Translation?
Let’s begin with the basics, what are social media translation services (SMTs) about? To define this service accurately, and truly communicate the value they provide the companies with, first we need to take a quick look at the role of social media in contemporary marketing.
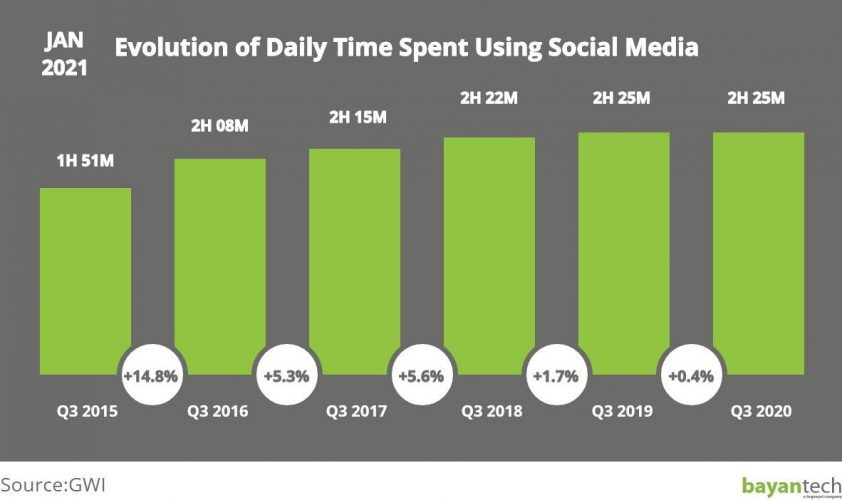
Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram… they all ring the bell, right? You are likely to be familiar with at least one of these popular social networks. It comes as no surprise that nowadays, pretty much every person regardless of age group, background, or location, has at least one social media profile. What’s more, according to Data Reportal, the average user spends 2hs 25min on social networks every day.
Social media is an excellent way for businesses to build brand loyalty and connect with customers because they are widely accessible platforms where you can engage with customers directly. This enables potential customers to see a more human side to your brand and to connect with you on a more personal level.
But the benefits don’t end just there. On top of that, the social media market is great to get a better understanding of what keeps customers engaged, and what doesn’t. It provides the opportunity to constantly sharpen and optimize your brand’s communication strategy through real-life, at-scale insights. A win-win situation.
So, if your company is working to expand to international markets, you should be planning to adapt your social media strategy and translate the content of your everyday posting and your social media campaigns as well.
Social media translation services make it possible for brands to connect to international audiences in a relevant and powerful way, through content that resonates with them. With social media translation services, brands can reap the benefits of social media marketing on an international scale.
Some Social Media Translation Best Practices
Considering the important role of social media in creating connections with your customers, adapting your posts and captions has to be taken as a serious social media translation project. But, how can you make the most out of your international social media strategy?
Don’t Rely on Machine Translation
At some point, you might have considered translating the little bits of text under your business’ Instagram photos with Google Translate. But it might not be a good idea.
Machine translation has indeed improved a lot in the past decades, and it can indeed be helpful from time to time (i.e. to check some vocabulary). However, it is not necessarily efficient when it comes to digital marketing.
The most common complaints about machine translation are all-too-frequent: since it doesn’t contemplate cultural nuances, it can miss important elements of your message and muddle up your words, leading -by default- to a severe alteration of the intended message and leaving room for severe misunderstandings.
But, how so? What are those cultural nuances? To give you an example, we could mention the phrase “I have a dream”. This sentence has a great historic and political weight in the US, whereas “Ich habe einen Traum” in German doesn’t have that same impact, it’s actually mundane.
Moreover, we could also take a look at the differences between some Spanish-speaking Latin American countries. Although they all share the same native language, they do not share the same background, therefore some words can differ in meaning from country to country. For instance, the word “limón” means “lemon”, and “lime” means “lima” in most of them, but in Colombia, it is the other way around. This is also the case for some slang words, which are insults in some countries but have a lighter connotation in others.

All in all, due to a wide diversity of cultural backgrounds, words or phrases can have a positive or neutral meaning in one region and a negative one in another.
And, since culture plays a key role when shaping a marketing strategy, if a poorly translated post gets published on your social media, you are running the risk of having your brand image damaged. Therefore, here is our first tip: Don’t completely rely on MT engines or other automated translation tools.
Localize Your Emojis
Emojis add meaning and complement the tone of a message. A quick digital marketing strategy hack: believe it or not, using emojis can not only contribute to your creative process but can also -and most importantly- can have a positive impact on the audience, leading them to engage more easily.
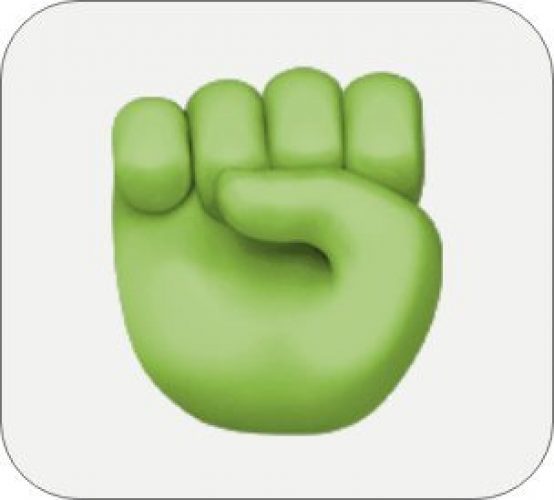
Nevertheless, it is worth considering that cultural sensitivities not only apply to words but also gestures and symbols, and emojis as well. A quick example of it could be a fist gesture. In a lot of places, it could represent fighting but, on the contrary, the Germans use it to wish each other good luck. Or the peace sign, which turns out to be quite offensive in the UK.
So, the way you approach social media Spanish translation projects, for instance, will differ from social media Tagalog translation projects. Different languages, different cultures, and different preferences to emojis.
So, with this in mind, here comes our second piece of advice: Pay attention to emojis, and localize them accordingly.

Do Local Market Research
To effectively address different markets through social media, you need to be well aware of who’s using what, how, and where.
As you already know, behavior patterns vary considerably from locale to locale, and social media platforms are no exception to this. Whereas some networks are quite a hit in some places, they can have a low impact or even be non-existent in others. For instance, according to Vincos, in Russia VKontakte is larger than Facebook, and the same happens with QZone in China.
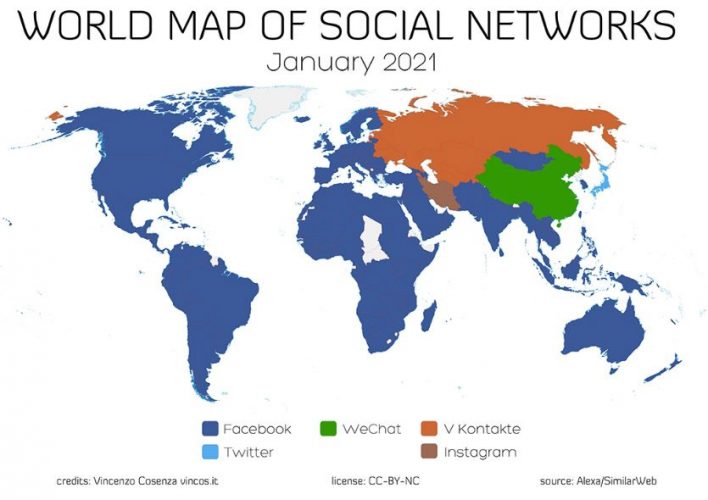
Furthermore, another factor that can differ between geographies is the way and purposes for which each platform is used. So, even though the previous statistic shows us that Facebook is the most used network around the globe, some countries might be more into sharing memes on the wall, and others might be making the most out of the marketplace feature. This is why localization is not only about translating posts into a target language, but also about knowing where and how to upload them.
This can be considered in the same light as SEO localization, in the context of website localization services.
Sign up to our newsletter to receive the latest blogs and news.
Have a Different Account for Each Place and Language
Considering our previous tip, it’s nothing to write home about that a specific account for each audience is a must. Having a single account, where everything is posted in multiple languages, is just messy and confusing for the reader. Plus, nine times out of ten, a lot of the content will be redundant for most of the audience, which will likely lead them to boredom and eventually to unfollow you.
And as that is the opposite of our intentions, having a specific account for each one of the locales will bring you great opportunities. It will enable you to address each target according to its nuances, likings, and demands, and to test their engagement.
So here comes our fourth tip: One size doesn’t fit all, craft a specific communication strategy and choose your portals according to your target audience.
Have Native Speakers in Your Team
Finally, it is good for you to distinguish what things should be translated from which things shouldn’t.
Beyond the digital marketing department, there is another one where linguistic and cultural accuracy is needed, and that is the customer support department.
When it comes to customer care, it is well known that to keep the client either happy or prevent them from getting more upset, it is better to address the issues as soon as possible.
Therefore, if a customer contacts you through a social media platform, you can not really afford the time to get a translator to check the messages that go in and out. Here is where a native-speaking crew can be useful. Who better to tell cultural sensitivities within just seconds than a native speaker?
Plus, native speakers in the translating and marketing team can serve as proofreaders for your content and help you shape clear plans for your strategies.
So, that’s our fifth tip: Bring in the locals.
Is Social Media Translation something you find difficult to address?
Work with Experienced Professionals
As you already know, making decisions about digital marketing translation and localization is not a light task. A lot of nuances must be taken into consideration, and so, deep research and a special eye for details are required. We know it can all sound a bit overwhelming, but don’t worry, here at bayantech, we are more than glad to help you through this process.
We are a leading translation company with almost two decades providing competitive marketing translation services. With deep cross-cultural insight, we offer social media translation services in hundreds of languages.
Whether you need social media in Arabic translation or social media in Urdu translation, our key focus is Middle Eastern and African languages. We also excel in Asian and European languages, so you can trust that social media in Chinese translation and social media in French translation, for instance, are within our scope of expertise.
We have proudly worked with top brands in the MENA region and beyond, surpassing expectations and delivering lasting positive results. Our success formula is simple: we put the latest cutting-edge technologies in the hands of a crew of native-speaking language experts, innovative engineers, working with ISO-certified quality assurance practices. No matter the project size or language pair, we can tackle the challenge.