Back in the day, machine translation models used to read words as numbers: 1 + 1 = 2. The issue with that? This mechanism stops working once a sentence gets a bit complex or has multiple interpretations. Since traditional MT views words as separate entities, users often end up with flimsy or even funny translations.
But with the invention of neural machine translation, MT improved so much that it became a reliable asset for translators across many projects.
In this article, you’ll learn what neural machine translation is, how it works, and how your business can use it for easier access to a global audience.
Why Neural Machine Translation Is Revolutionary
While human translation is unrivaled in quality, it has its shortcomings in the business world. On average, a human translator can process around 2,500 words per day, something that can become a drawback for large-scale projects and tight deadlines.
Additionally, human errors such as typos or inconsistent translation of similar terms can take significant time for reviewers to detect and fix. All of this adds to the total cost of a translation project, which varies depending on the language pair involved.
NMT, with its refined, brain-like processing of text and context, has become a revolutionary solution to these challenges. And while NMT has its own limitations, when paired with human expertise, AI-powered translation truly transforms the field.
This global shift toward using AI for translation efficiency is reflected in a report by Forbes, which states that 44% of businesses are planning to incorporate GenAI for translating content into other languages.

How Does Neural Machine Translation Work?
The word neural refers to how this technology is designed to imitate the human brain, working with a network of “neurons” to connect the dots and provide context to deliver accurate translations.
Here are some key features of NMT:
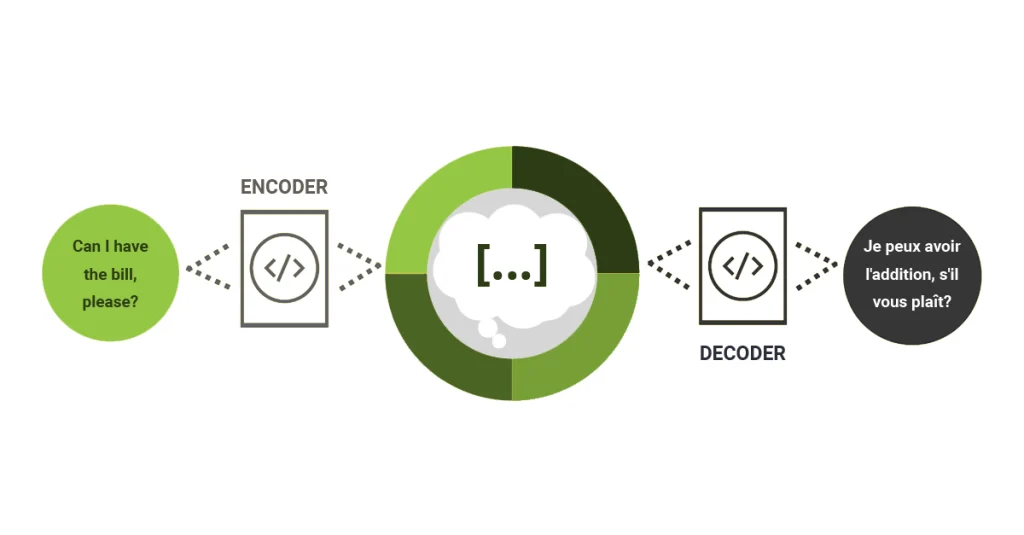
Encoder-Decoder Architecture
How does NMT work? It encodes sequences in the source text, “understands” those sequences like the human brain would, and then decodes them in the target language.
This process follows what’s known as a sequence-to-sequence model, a foundational approach in modern NMT. Transformer-based NMT is one of the most advanced architectures built on this concept.
Attention Mechanisms: Why Context Matters in Translation
Another feature of NMT models is their use of attention mechanisms. These mimic human focus on context to produce the correct interpretation of words. For example, the word bank could refer to a financial institution or the side of a river, depending on the context.
BLEU Scores: Measuring Accuracy
BLEU scores are a quick way to measure how close machine translation is to human translation. They work by comparing n-grams between the two. The more matches, the higher the score. It’s widely used, though not perfect, as it doesn’t fully capture meaning or fluency.
Training NMT Engines: The Role of Parallel Corpora & Embedding Layers
Neural Machine Translation engines learn from parallel corpora, sets of sentences that are translations of each other in different languages. These help the model understand how words and phrases align across languages.
Embedding layers convert words into numerical representations that capture their meaning, allowing the model to process them effectively. When multilingual datasets are used, the NMT engine can learn patterns from one language and apply them to another.
This is called cross-lingual transfer, and it’s especially helpful for improving translation quality in languages with less available data.
This is also where zero-shot translation comes in—an advanced capability of some NMT systems that allows them to translate between language pairs they haven’t been explicitly trained on. This makes it particularly valuable for low-resource translation tasks.
5 Reasons Global Businesses Choose NMT Over Traditional Methods
- Speed
When businesses need to launch their international app or website within a short time frame, NMT steps in as a solid solution, especially when paired with services like MTPE to ensure accuracy. It’s particularly useful for automating the localization of number formats, currencies, and product descriptions.
- Scalability
Scaling up for large projects means incorporating NMT to streamline the translation process. Depending on the industry and type of content, NMT can play either a small or major role.
For example, allowing NMT to handle manuals, product descriptions, or date formats, followed by human post-editing, is an efficient and practical approach.
- Cost Efficiency
The rates for MTPE services are significantly lower than those for traditional translation, which helps reduce costs, especially for content that NMT can handle easily and accurately.
- Applicable to Less Common Languages
When localizing projects into less common languages, finding a large pool of professional native translators can be difficult. In these cases, NMT can take over and process content in rare languages efficiently.
Types of NMT Systems and Their Usage
There are two main types of NMT systems: ready-made and custom.
- A ready-made NMT system, like DeepL, is fast and easy to use but isn’t tailored to a specific type of content or industry.
- A custom NMT system is trained using your own content. It’s fed with terminology bases and information about your brand’s tone and voice, making it fully tailored to your specific needs.
NMT models can also operate using two main techniques: BART translation and beam search decoding.
- BART translation is ideal for creative content like marketing, where tone and variation matter.
- Beam search decoding delivers more precise translations for technical and structured content, such as manuals.
3 Steps to Integrate NMT into the Translation Workflow
Here’s how a professional LSP uses NMT effectively:
- Auditing ContentIdentify which content types are suitable for machine translation. For example, eCommerce content types like product descriptions and customer reviews, or automated customer service messages, are ideal use cases for NMT.
- Selecting EnginesChoose different NMT engines based on the content type. For instance, use multi-modal translation for videos that require both subtitles and localized on-screen text.
- Training TeamsCollaborate with your localization or linguist teams to train them on how to effectively use and post-edit NMT output. This helps tailor the final content to match each brand’s tone, style, and niche.
5 Signs Your Business Needs Neural Machine Translation
- You’re expanding into new markets quickly.
- Localization costs are growing unsustainably.
- You need to translate multimedia content at scale.
- Your content volume exceeds what your human translators can handle on time.
- Consistency issues in terminology and style across multiple languages are affecting your brand image.
While Google Translate works well for general content, enterprises often require tailored machine translation services to handle industry-specific jargon.
This is because Google Translate’s neural models are built for broad multilingual coverage, not for the domain-specific accuracy businesses often need.
Translate with bayatench
Our team of native translators and linguists offers a wide range of services, prioritizing quality and efficiency. Whether your business needs thorough human translation or MTPE services, a dedicated project manager will guide you throughout the process, assessing the right translation or localization solution for you, ensuring your project is delivered on time and tailored to your needs.