8 Steps Every Medical Interpreter Takes
Looking for a medical interpreter? Discover the career path of medical interpreters and qualifications they need to acquire to take on interpreting jobs.
Imagine after months of hard work promoting and marketing your localized software and the big day arrives — you launch it to the new market. However, to your disappointment, users begin to experience frustrating technical issues that drive them away with negative first impressions.
How to prevent this? By performing localization testing before your software kicks off.
What Is Localization Testing?
Localization testing is the process of testing software, whether a website or an app, to ensure that it meets the cultural, usability, and legal requirements of a specific region and target market. Simply put, it means that you simulate the user experience to see how your software applications will perform in real life.
As such, localization testing helps you identify any errors that may impact the user experience at any touchpoint and fix them before launching. This includes the language, layout, functions, privacy policies, and more. Localization testing ensures the final product meets user expectations and complies with local laws and regulations.
When it comes to localization testing, there are different steps, each with a specific focus and purpose. So, without further adoو let’s jump to the next point to understand what the localization testing process looks like.
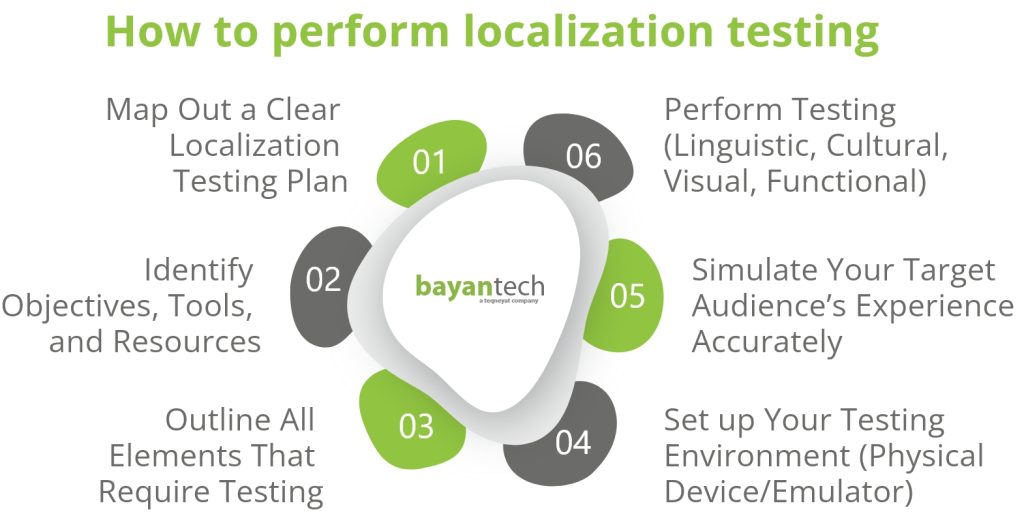
How to Perform Localization Testing
1. Set up a Testing Plan
First things first, you need to set up a clear localization testing plan, including the objectives, tools, and required resources. You should start by mapping out the objectives and scope of the testing process.
Then, outline a detailed checklist of all the different aspects and features that need to be tested including visual and layout elements.
Finally, identify the required human resources and tools. Decide if you’re going to team up with a localization partner and choose the testing tool you’re going to use.
2. Prepare the Testing Environment
After outlining a clear plan, the next step is to set up the test environment. It’s crucial to build a test environment that identically mimics how and where the end-users will experience your site or app, to ensure tests are realistic and identify any issues they may encounter.
Whether conducting tests on physical devices or via emulation software, establish an environment that accurately reflects your users’ typical conditions. Consider factors like your audience’s physical location, most commonly used devices, their preferred browsers, etc.
3. Test
Once everything is planned out and tools are in place, you can begin the localization testing process. There are four types of testing you should perform.
- Linguistic testing covers the quality of translation and linguistic aspects. It verifies that translated content is linguistically correct and appropriate for local users. Linguistic testing involves double-checking the text to fix any grammar, spelling, or punctuation mistakes.
- Cultural adaptation testing focuses on the cultural relevance of the content, making sure it’s culturally appropriate and does not offend the target audience. This includes images, color schemes, icons, and other content that could be culturally sensitive.
- Visual testing ensures that all visual elements are correctly displayed in localized versions. The goal is to verify that all textual content fits properly within the interface elements like buttons, menus, and dialog boxes with no layout issues.
Functional testing checks whether the software operates as intended. It involves validating features, workflows, and functionalities after the application has been localized. This could include date and time formats, currency calculations, and other region-specific elements.
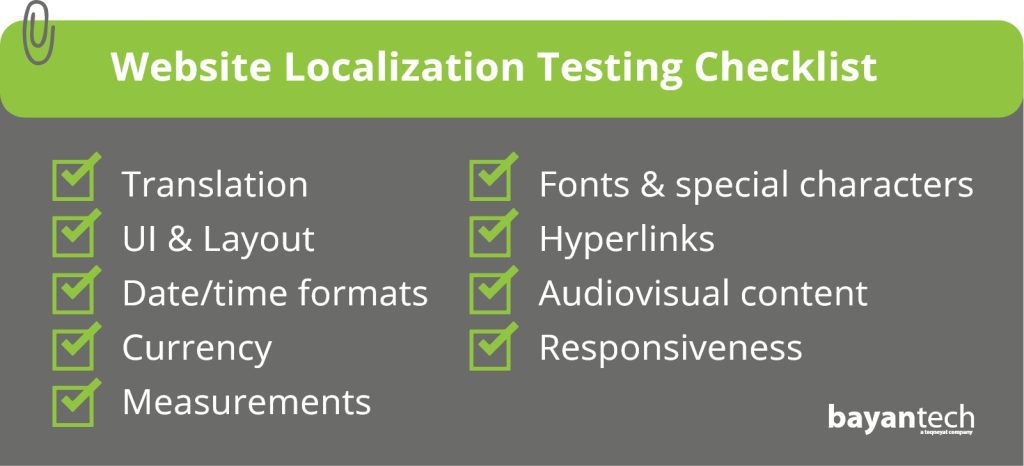
Website Localization Testing Checklist
Let’s break down the website localization testing process and everything you should cover for successful localization outcomes.
Translation & Textual Content
Your localization testers should validate the quality of translated content, making sure that it’s linguistically accurate, grammatically correct, and culturally appropriate. All cultural references, taglines, and marketing copies should resonate with your target users and language must flow naturally and coherently.
UI and layout
Test user interface elements like buttons, menus, and icons across different screen sizes. Check text wrapping, spacing, and alignment. Ensure that all visual elements fit properly in the layout and that there is no cramped or overlapping text post-translation. If you’re localizing into RTL (right-to-left) languages, make sure that the text flows correctly and in the right direction.
Numbers, Date & Time Formats, Currency
Double-check all locale-specific elements that differ from one region to another and ensure everything matches local conventions. This includes date and time formatting, currency format, measurement units, number formats, and decimal separators.
Fonts and Special Characters
Localization testing involves scanning through your entire website for any incorrect formatting of fonts or special characters across different writing systems.
Audiovisual Content
Verify that all your localized multimedia elements load properly, such as images, animations, video, and audio content. You should also confirm that they don’t involve any inappropriate messages or negative connotations that might offend the target locale.
Functionality
Thoroughly test all site features, interactivity, and responsiveness functions and confirm that navigations are intuitive in the localized version. Your localization testing process should also involve checking whether the hyperlinks on your site (inbound or outbound) send users to correctly localized pages. You don’t want to lose users to broken links.
How to Perform Mobile App Localization Testing
Performing localization testing for mobile apps is a similar process to testing a website or software and involves the same steps. However, there are other key considerations to factor in when testing your localized app.
- Test your app’s compatibility and responsiveness on different screen sizes and operating systems.
- All text elements such as app names, descriptions, marketing, onboarding screens, and in-app tutorials must be tested in the target language.
- Verify push notifications and in-app alerts are formatted correctly in the localized version.
- Check localized resource file sizes and their impact on install size and load times.
- The app update experience must be validated and tested for any code changes or emerging bugs.
8 Steps Every Medical Interpreter Takes
Looking for a medical interpreter? Discover the career path of medical interpreters and qualifications they need to acquire to take on interpreting jobs.
bayantech: Localization Partner You Can Trust
bayantech is a leading provider of language services with over 20 years of experience serving various global and regional brands across industries. We strive to offer comprehensive localization services powered by native-speaking experts with extensive technical and linguistic backgrounds.
At bayantech, we follow a rigorous quality assurance process at each stage of the localization workflow. Also, our services conform with ISO 9001 and ISO 17100 certification standards, guaranteeing our clients high-quality results they can rely on.
Contact us today and learn more about our processes and solutions!