88% of shoppers won’t return to a site after one bad user experience.
Yet, too often businesses overlook how cultural and linguistic differences shape the user experience when translating their software. This usually makes their entry into foreign markets more challenging, leading them to miss opportunities to grow their market share.
Software localization bridges this gap by creating an intuitive experience that satisfies local user expectations and caters to their unique preferences in their native languages.
So, in this guide, we have compiled everything you should know about software localization to strategically expand into new countries.
What Is Software Localization?
Software localization is the process of adapting software to the linguistic and cultural requirements of a specific target market. The goal is to design and develop a software product that feels like it was made with a particular audience in mind.
As such, localization takes a comprehensive approach and requires more than just simply translating strings of text. It involves tailoring all user-facing content including the software’s textual content, user interface (UI) design, and user experience (UX).
The Software Localization Process in 4 Steps
Let’s explore what the software localization process looks like and what it involves.
1. Preparation & Pseudolocalization
Before the localization process kicks off, planning and preparation are a must. This involves assessing the source material and identifying potential challenges that the localization teams might face.
For example, if you’re approaching localization after you have already developed your software, you are more likely to encounter layout issues such as text expansion. This typically happens in translation because some languages take up more space than others.
To avoid this, your localization partner must perform pseudolocalization. This is a testing method to simulate the size and shape of the translated text. By doing so, they can address technical issues early on and design a layout that can seamlessly accommodate several languages
2. Text Translation
Once everything is planned and your software is ready, it’s time to extract all content that requires translation such as menus, dialog boxes, labels, and error messages. After uploading the content into the translation management system, linguists work on the translation while paying attention to cultural nuances.
3. UI & Media Localization
At this stage, designers and engineers work on adapting user interfaces and visual elements to the technical and cultural requirements of your target locale.
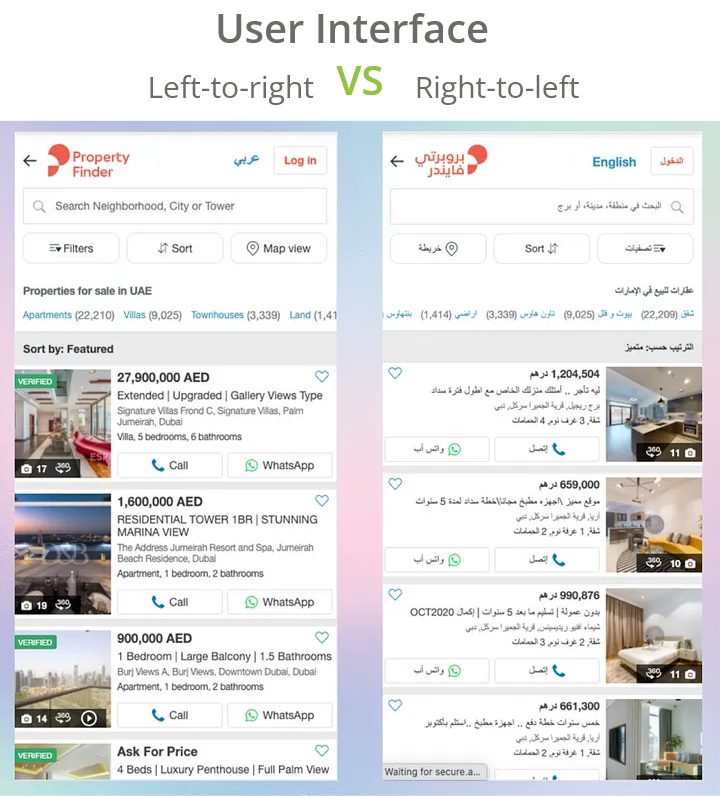
For example, right-to-left languages, like Arabic and Urdu, require you to modify the layout and text direction. Fonts also need to support different writing systems. What’s more, date and time formats should match local conventions to avoid confusing users.
Additionally, audiovisual content is adapted to reflect local preferences and cultural norms. From graphics to videos and voiceover, your localization team should ensure that everything is culturally appropriate and relevant to target users.
4. Testing & Quality Assurance
After the translation and localization process is complete, your team performs linguistic and technical quality checks to confirm that all textual and visual aspects are appropriate and accurate.
Also, this stage involves market testing to assess how local users interact and engage with the final product and whether it meets their expectations.
Dive deeper into the process of designing multilingual software in our blog post: The Essential Guide to a Successful Software Localization Process!
Software Localization Tools to Optimize & Speed Up Your Workflow
When entering new markets, efficiency and speed are key players. For this reason, using localization and translation tools is essential to avoid bottlenecks and give you faster time to market.
Translation management systems (TMS) are designed to assist human translators and automate the localization process. Most importantly, by integrating effective tools within the TMS, your language partner can further maximize quality and efficiency. Here’s how:
Computer Assisted Translation (CAT) Tools
CAT tools provide a central platform to manage translation processes from start to finish. They help organize materials, track progress, and coordinate between translators, project managers, reviewers, and clients. These tools only assist human translators and are not used to machine-translate your content.
Translation Memory (TM)
Translation memories store previously translated and approved phrases, allowing translators to automatically reuse them for repetitive segments. This not only saves time by speeding up the translation process but also ensures the consistent use of terminology across all materials.
Automated Quality Checks
One handy feature in CAT tools is its built-in automated quality checks. It’s very effective in catching spelling and formatting mistakes to guarantee that the final output is error-free. Nonetheless, it still doesn’t replace human oversight and proofreading done by subject matter experts.
Glossary and Termbases
Glossaries and termbases are a list of specific terms paired with their pre-approved translations, either created by you or in collaboration with your language partner. This gives translators direct access to approved terminology and style references enabling them to improve their productivity and reduce research time.
Software Localization Best Practices for a Successful International Upscale
By now, you might be feeling that taking your digital product global is a quite daunting task. But it doesn’t have to be so as long as you follow strategic moves. These effective tactics will grant you seamless success across markets.
Keep Scalability in Mind
Building efficient and scalable localization workflows from the start is critical for your business’s success. And it’s especially crucial if you’re in an industry where time is a key factor.
Scalability means you can easily adapt to growing demands and add new languages and regions without investing more time in reworking and redevelopment. So, how can you do this?
Firstly, you should consider internationalization. This means designing a neutral product that you can easily adapt for international users. For instance, you can start by removing culture-specific elements that require heavy adaptation. You can also keep translatable strings separate from source codes in resource files.
Furthermore, implementing translation tools, which we have mentioned earlier, is also very effective. If you work with a professional translation company, you can easily build a translation memory database and glossaries that will help automate localization.
Test Early, and Often
Any software development process is prone to bugs and errors. However, when entering a new market, it’s critical to catch them before your product goes live, or else you risk damaging your brand image.
This is why thoroughly testing your final product’s usability and compatibility with local requirements is super important. Also, approaching localization testing as an ongoing process is crucial. Why? Because users’ behaviors and habits are always changing and new technologies emerge over time.
Additionally, frequently testing and adapting to market changes helps you stay relevant to target users and their evolving needs, making them feel valued and respected. Ultimately, this helps you keep customers loyal to your brand, giving you an edge to outperform your competitors.
Your Localization Testing Cheat Sheet
Get insider tips on how to catch localization errors early to save your time (and money) in one handy guide.
Harness The Expertise of Localization Specialists
Successful software localization takes more than accurate translations. You need deep technical and cultural knowledge in addition to efficient processes and management tools. This is what makes localization service providers worth the investment.
When you partner up with a reputable language partner, you get more than just professional translators. You’re also investing in the infrastructure and systems they have built over the years serving numerous clients while maintaining the required quality standards.
With domain experts, fluent in your target language, you can trust that your software is culturally resonant, linguistically accurate, and technically compatible with market requirements.
Furthermore, reliable translation companies will integrate into your software development workflow to streamline everything and deliver a high-quality output that meets your timeline and expectations.
Want to discover more effective localization tactics? Check out our complete guide: Software Localization Best Practices.
bayantech: Software Localization Services Tailored to YOUR Needs
bayantech is a leading language service provider with over two decades of experience specializing in software, games, website, and app localization across +120 languages.
We provide fast, accurate, and cost-effective software localization services customized to your specific needs. Over the years, bayantech has guided many global and regional brands on their journeys across borders.
We solely rely on a hand-picked team of native-speaking translators, localization engineers, designers, and developers. Thanks to our ISO-certified quality management systems and advanced translation tools, you rest assured that your materials are handled with professionalism, confidentiality, and precision.
Contact us today and let’s discuss how we can help your brand
8 Steps Every Medical Interpreter Takes
Looking for a medical interpreter? Discover the career path of medical interpreters and qualifications they need to acquire to take on interpreting jobs.