Your business is doing great locally, and now you are planning to take it one step further into new global markets.
One important thing you need to know is your global customers are expecting more than getting easy access to your products and services. They are expecting to get them in their native language.
And you know what they are expecting even more? To feel that what you are offering is originally made for them, adapted and personalized for them based on their culture and preferences.
So, is it localization vs. internationalization? Or both? If you aren’t sure, this blog post is for you.
Let’s dive in.
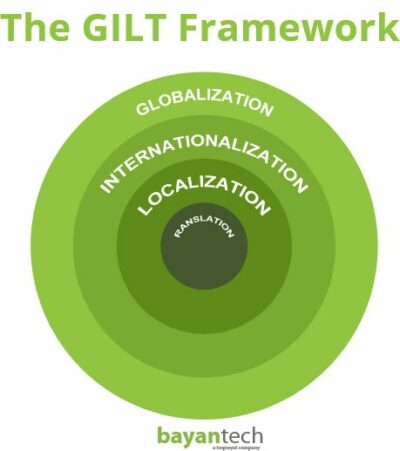
Localization vs. Internationalization
What Is Internationalization?
The term internationalization, also known as “i18n,” refers to the design and engineering of software products so that they can easily be localized for different multilingual markets.
The main goal of internationalization is to create modular products that are culturally neutral so that they can effectively be adapted to support multiple languages, cultures, and other locale-specific components.
We can simply say that internationalization is the process that paves the way for localization to happen.
Here is a quick glimpse into the key practices internationalization entails when preparing software products for global use.
4 Key Practices of Software Internationalization: The How
1. Basing The Software On The Unicode Standard
You want to make your software product universal, which means that it should support almost all languages.
For that to happen, a successful software internationalization process leverages a large character encoding system, which prepares the software codebase to receive various configurations based on your target language.
While ASCII character encoding has been great with most Western European languages, languages like Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Russian, and Hindi required larger character encodings like Unicode.
The creation of the Unicode Encoding Standard has facilitated the process of software localization to a greater extent.
This encoding system encompasses all characters used in all modern languages including Arabic, which helps make your software-displayed text readable after translation, and ultimately allows your software products to be adapted to literally every area of the world.
2. Adapting Code to Recognize Cultural Differences
A very important step in software internationalization that prepares for an easy localization process is for the software developer to adapt your software code to recognize cultural differences and divergences in language rules.
To do so, you have to incorporate localization data and culture-specific components into your software source code library.
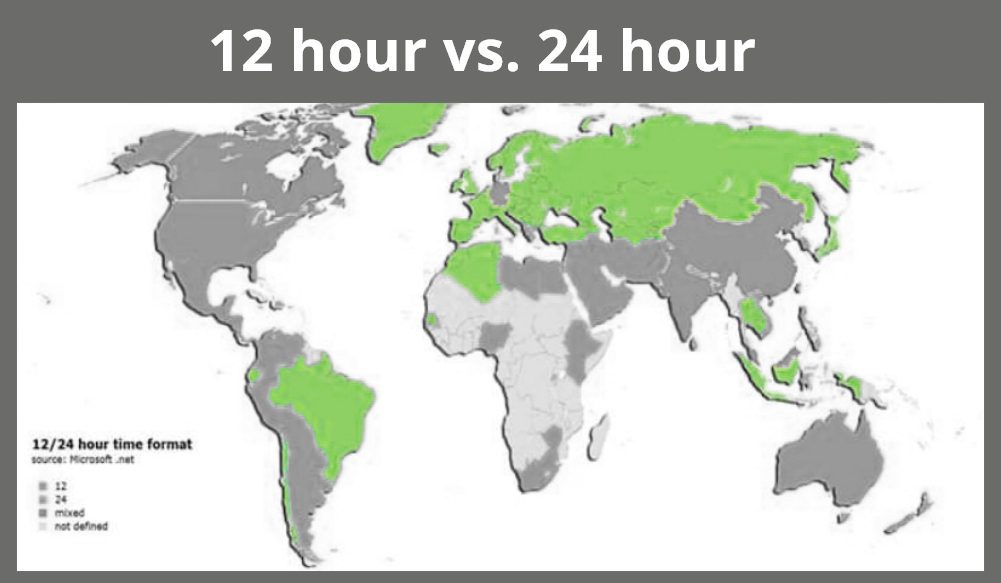
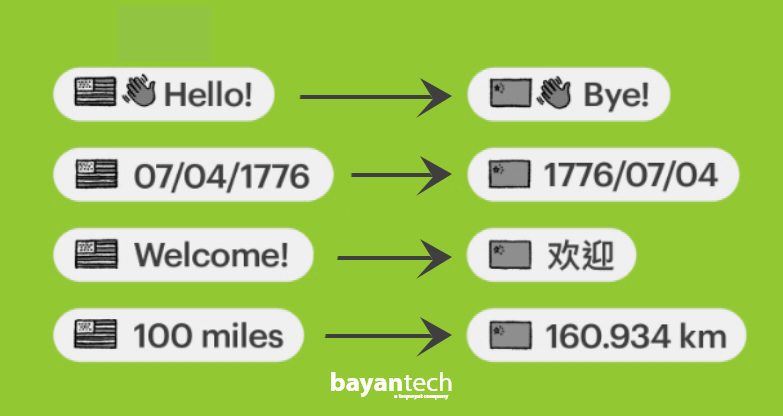
Cultural differences affect number formats and numeral systems of elements like date and time format as well as currency. Some countries, for example, adopt the 12-hour clock format while others follow the 24-hour clock format.
3. Adapting User Interface (UI) for Variations in Text Length
Considering text length variation is another key practice for software internationalization. Internationalization will help you adapt your software user interface for variation in text length after translation to avoid issues associated with text expansion, for instance.
When you translate text into the language of your target audience during the localization stage, text expansion is usually one of the challenges you will encounter. And it can actually be time consuming to handle if your software has not been prepared for it earlier.
Text expansion occurs when the text expands and the number of letters increases, after translation, to the extent that the text overflows within other UI elements including buttons, menus, and text boxes. And unless it is accounted for, it can lead to several layout issues like text misalignment and text truncation.
This is a real challenge as it can badly affect the readability and usability of your software, which can be confusing and frustrating for users who might find it difficult to navigate through it.
However, with the help of the in-context reviews feature, software engineers and translators ensure that the translated text fits within the character limit in the context of the software’s UI elements.
4. Organizing Source Code Via String Externalization
Sounds really complicated, doesn’t it? Let us put it simply.
String externalization is the process of separating translatable text and localizable elements in your software application to store it outside the source code. This is typically done to facilitate importing and exporting the text for translation without affecting the rest of the code.
After extraction, the strings are saved in certain file formats that translators can easily access during translation and localization.
This is one of the crucial practices of internationalization that need to be carried out early because leaving it until the actual localization will definitely be time, effort, and also money consuming.
What Is Localization?
Also known as “l10n,” localization is the process of adapting products to meet the language and culture as well as the technical and legal requirements of a specific target audience.
When it comes to software localization, the process involves translating content, adjusting it to cultural references, and modifying the software’s UI and visual elements, while optimizing the software’s performance and functionality.
The main goal is to create a final version of your software that seems and feels local to your target audience as if it was never translated, as if it is made specifically for them.
Curious to know how localization achieves this? Let’s explore some of the practices localization entails.
3 Key Practices of Software Localization: The How
1. Content Translation
Content translation involves converting the textual and audiovisual content of a software application from one language to another. This involves translating the following:
- All text-based elements
- Instructional text
- Audio or video content
Effective software content translation requires not only linguistic proficiency but also a deep understanding of the intended audience to fit their cultural norms and expectations.
This includes taking into account factors like differences in time and date formats, currency, units of measurement, and other cultural factors that impact how software is used and understood.
Translating your software content boils down to creating a fully localized experience – a fully personalized experience.
If the content of your app or website sounds like a mere translation of your original content, the whole experience would be strange and alien to them. And when that happens, you won’t be able to elicit an emotional response from your users enough to convince them of what you are offering them as well as your brand.
The aim of your app or website content translation is that it shouldn’t sound like a translation at all.
2. UI/UX Localization
This practice involves adapting the user interface and user experience of a software application including elements like the layout, color scheme, and other design elements.
Although it sounds like a simple task, it actually requires a deep understanding of the target market’s cultural and linguistic preferences to be able to design an intuitive and user-friendly experience. Here are 3 major aspects that UI/UX localization considers.
- The design, layout, and visual elements of the software to reflect the cultural norms, values, and preferences of the target audience
- The functionality and user experience of the software to reflect the local user behavior, including device usage, browsing habits, and payment preferences
- Software usability to work on different devices, platforms, and networks, ensuring that it complies with local regulations and standards
3. Localization QA & Testing
Localization testing in software is a key process carried out to verify that the software that has been localized for a specific region or culture meets the quality standards and requirements of that region or culture.
Localization QA and Testing (LQA) involves checking that the localized content, design, and functionality of the software application are accurate, appropriate, and user-friendly for users in the target market.
Here are some key aspects of software localization QA and testing:
- Linguistic Testing: Checking the text content of the software to make sure it is free of any linguistic inaccuracies. This includes verifying spelling, grammar, and punctuation.
- Cultural Sensitivity Verification: Verifying that both content and design, including visual elements such as colors, symbols, and photos, are culturally appropriate and do not have negative connotations that imply cultural insensitivity and offense to the target audience.
- Functionality Testing: Ensuring that the localized software application works as intended and is compatible with the target platform, device, and network.
- User Experience Testing: Making sure the localized software provides a seamless and intuitive user experience for users in a specific target market by testing aspects such as readability, usability, and accessibility.
- Compliance Testing: Confirming that the software meets requirements related to privacy, security, and accessibility to ensure that it complies with local laws, regulations, and industry standards
- Regression Testing: Verifying that localization changes have not impacted the functionality of the software that was working correctly in the source language version.
Localization vs. Internationalization vs. Globalization in a Nutshell
A Checklist for Effective Localization And
Internationalization Testing
Don’t let poor testing hold you back from your software’s global success. Get this comprehensive checklist to guide your efforts.
l10n vs. i18n: The Why
Why Is Internationalization Critical for Your Product’s Global Success?
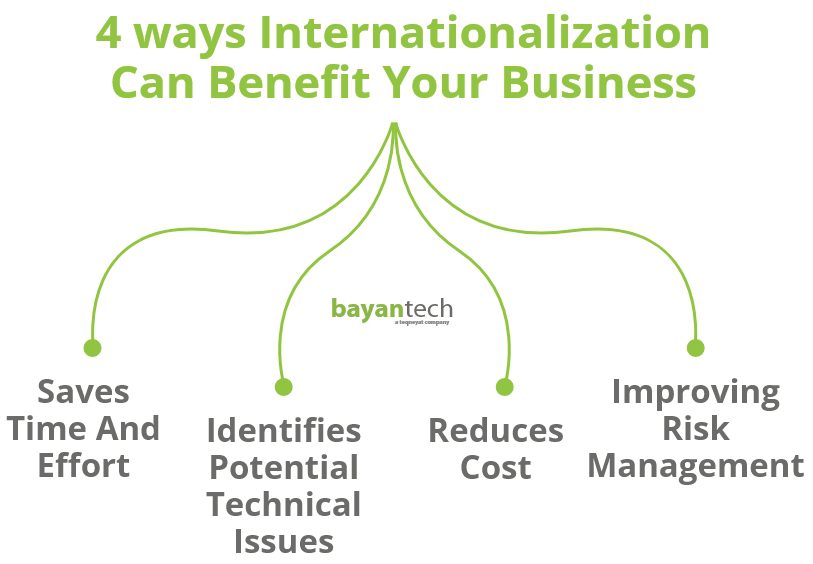
Saves Time and Effort
Internationalization helps you prepare your software for global use. In doing so, it ensures that no major technical challenges can ever stand against localizing it to fit any target area.
Since it already lays the foundation for your localization process, it eliminates the need to make significant changes or fundamental engineering modifications to the software in the future when localization is actually happening.
This helps to reduce time-to-market significantly and gives your business the advantage of being more agile when it comes to time-based competition. Not only time but internationalization also saves you the effort of starting from scratch every time you want to target a new region.
Facilitates Identifying and Fixing Technical Issues Early
Internationalization also enables you to identify any technical issues earlier before they occur during the localization process. This helps you prevent such issues from happening, rather than resorting to re-engineering the software to fix them.
For example, identifying an issue like breaking the UI due to text expansion can be avoided by adapting the UI for variations in text length in the early stages of designing the software.
Improving Risk Management
Internationalization means that you are preparing your software product to operate literally in all global markets. If one fails you, the others won’t.
Market diversification is one of the significant advantages of international business, and internationalization offers you this advantage on a silver plate. By adapting your software product to serve various multilingual global markets, it enables you to be less dependent on one single market which is great.
After all, putting all your eggs in one basket is always risky.
Reduces Cost
Yes, you might be investing to develop an internationalization strategy to globalize your software products; however, it definitely pays off in the long run.
Internationalization allows you to avoid future challenges like technical issues which saves you the financial cost of restructuring your source code or making any sort of significant technical interventions during the localization stage.
Why Localization Is Your Access to Global Markets
Improves User Experience and Increases User Satisfaction
When it comes to software localization, user experience is always the endgame.
Localization ensures that your users can seamlessly interact with your software product, feeling that it is designed specifically for them, from app content to UI. Such a blend of localization and personalization drives optimal user experiences.
Just give your users a local experience, and watch them return to you every time.
Boosts Brand Visibility and Sales
Localization is great, but with localization and SEO optimization, you are unstoppable. With SEO localization, your app/website is more visible to users when they search in their native language for similar products.
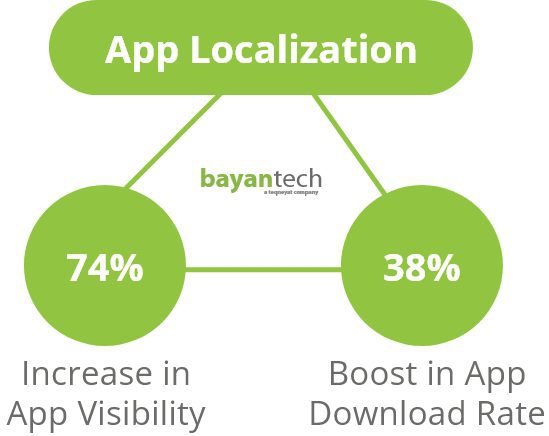
A recent study on the impact of localization on AutoScout24.ch, the most popular car app in Switzerland, has shown that localization has increased the visibility of the application by 74% and boosted its download rate by 38%.
If your product is a mobile application, for instance, localization can boost your app’s visibility and the number of installs. And with more visibility and downloads across different markets, localization can also boost your sales significantly as it increases the likelihood of more people browsing products, adding items to their cart, and completing purchases.
Gives You A Competitive Advantage
Global competition is tough. But being a foreign business tapping into a new local market, standing up against local competitors is actually tougher.
You know people tend to prefer getting products and services in their native language. Imagine how lucky you can be if you give them that with a touch of cultural relevance that transforms your foreign product into a local one. The thing that can drive them to choose you over other competitors over and over again.
Localization vs. Internationalization: bayantech Offers Both to Support Your Global Expansion Efforts
Want to make the most of internationalization (i18n) and localization (l10n)? You’ll need bayantech on your side.
bayantech is a leading translation and localization company, offering high-quality software and content localization services to support your global expansion efforts. From localization experts to cutting-edge localization and translation technology, bayantech is equipped to provide professional, customized solutions to take your products global.
Our professional team works with ISO-certified best practices and implements robust QA and localization testing to ensure the utmost quality.
Contact us today to know more about our variety of services and how our expert team can help you with your upcoming localization project.
8 Steps Every Medical Interpreter Takes
Looking for a medical interpreter? Discover the career path of medical interpreters and qualifications they need to acquire to take on interpreting jobs.